G-Wizard Documentation
User Guide
More Useful Resources
How to Solve the Hardest Problem in Feeds and Speeds Easily:
This video takes you through how to get started in Feeds and Speeds with G-Wizard. It turns out, you want to tackle the hardest problem first, and that’s deciding on the best Cut Depth and Cut Width. G-Wizard has a proprietary feature called CADCAM Wizards that solves this important problem nobody else has good answers for, and we show you how it works.
What are CADCAM Wizards?
CADCAM Wizards are a revolutionary new way to think about Feeds and Speeds introduced by CNCCookbook. They use AI Machine Learning Algorithms to optimize your Feeds and Speeds. They work by capturing expert machinist's knowledge into AI Algorithms and augmenting those with the Cutting Physics Engine built into the Feeds/Speeds tab in G-Wizard Calculator.
What makes them unique is they require far less data input than conventional Feeds and Speeds calculators yet they can produce far more optimal results. Pretty cool, eh?
Anatomy of a CADCAM Wizard
The UI of CADCAM Wizards change based on what type of feature you're machining. For example, the UI for machining a pocket is different from 2D Profiling or machining a hole. Also, the list of wizards available changes depending on whether you have selected a Mill/Router or Lathe machine.
But, the general layout of each wizard is the same. Here's a CADCAM Wizard for Pockets with the basic areas labeled:
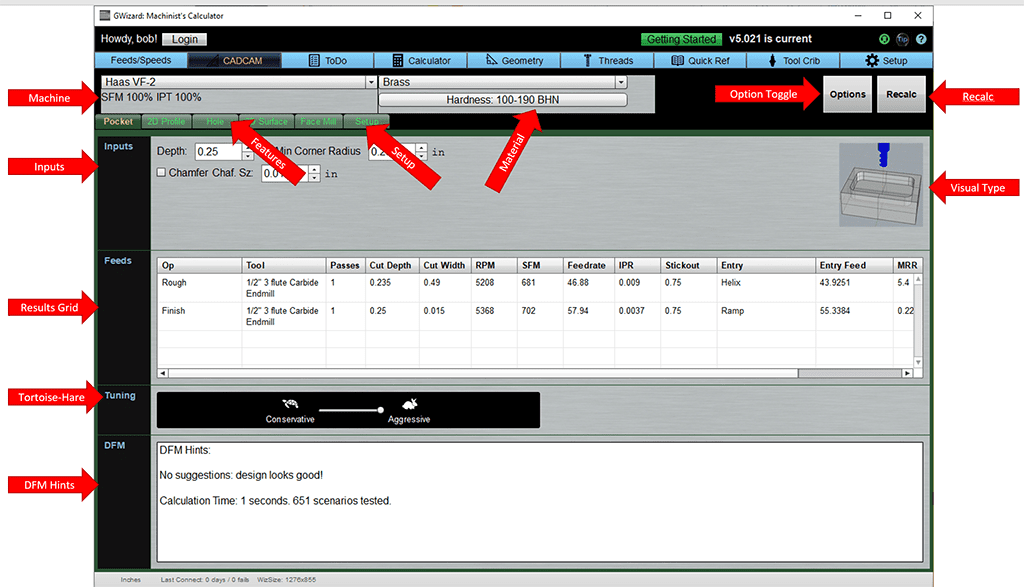
Here's the function of each area labeled with a red arrow:
- Machine: Select the machine you'll be using. It's the same as the machine selector on Feeds and Speeds and they're linked to keep the same machine.
- Material: Select the material you'll be cutting. It's the same as the material selector on Feeds and Speeds and they're linked to keep the same material.
- Options Toggle: Opens an Options Pane that shows additional options for this CADCAM Wizard. The Options Pane appears below the Inputs.
- Recalc: Recalculate the CADCAM Wizard. Recalculation of CADCAM Wizards is always manual.
- Features: Determines which CADCAM Wizard is selected based on what kind of part feature you need to machine. The feature list is different for Mills/Routers vs Lathes.
- Setup: Overall Setup Options for CADCAM Wizards.
- Inputs: The Inputs specific to this feature.
- Visual Type: A visual idealization of what kind of feature will be machined.
- Results Grid: The Feed and Speeds "Recipe" result from the CADCAM Wizard. Blank until you press "Recalc".
- Tortoise-Hare: Allows you to make the CADCAM Wizard more conservative.
- DFM Hints: Hints to make manufacturing the feature cheaper. Also tells if there are errors that prevent CADCAM Wizards from finding a result.
CADCAM Wizard Setup Options
Click the "Setup" tab to access the CADCAM Wizard Setup Options. There are 2 different Setup Option screens. One for Mills and Routers, and one for Lathes. The one you see is based on what kind of machine is currently selected. If there is a mill or router selected, you'll see options for mills and routers. If a lathe is selected, you see the lathe setup options.
Mill Setup Options
Here is the Mill Setup Option screen:
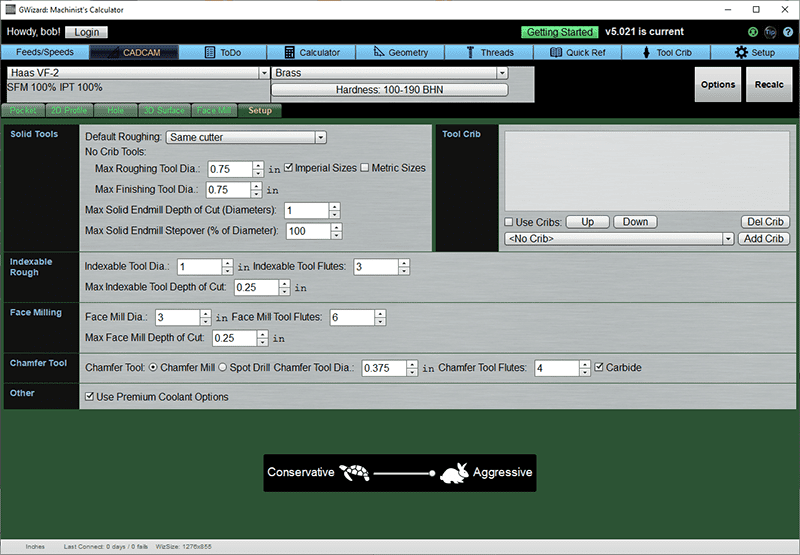
Here's what the Options do:
Solid Tools
This section tells CADCAM Wizards roughly what sizes of Solid Endmills are available in your shop and what Roughing Strategy you prefer to use.
Endmill Sizes
You get to specify the maximum size of roughing and finishing tools, as well as whether you carry Imperial and/or Metric sizes. You can also specify the maximum depth of cut in diameters (default is 3) and the maximum stepover (default is 100%). Don't mess with the max depth or stepover unless you know you need to go a lot more conservative than G-Wizard's defaults for some reason.
Roughing Strategy
The "Default Roughing" allows you to specify your preferred default roughing strategy from these choices:
- Same Cutter: Use the same solid endmill for roughing and finishing.
- Same Cutter + HSM: Use the same cutter, but use an HSM toolpath like Adaptive Clearing or Volumill for roughing.
- Corncob Rougher: Use a Corncob (Serrated) for roughing and a regular solid endmill for finishing.
- Corncob + HSM: Use Corncob plus an HSM toolpath like Adaptive Clearing or Volumill for roughing.
- Large Rougher: Use a larger sized Rougher then a smaller finisher. This requires your CAM software supports Rest Machining so it knows what was already machined by the larger rougher.
- Larger Rougher + HSM
- Larger Corncob
- Larger Corncob + HSM
- Indexable Rougher
- Indexable Rougher + HSM
I'm sure you can follow what the options I didn't label do given what the others do.
So, how do you know which one to pick? We have a whole article on roughing strategies, but here's a picture that may be worth a thousand words:
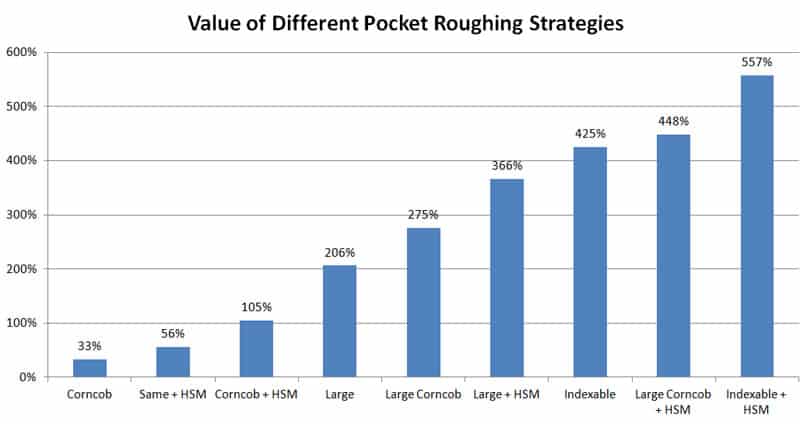
Those numbers are for aluminum and show how much faster the strategy was over just using the same solid endmill for roughing and finishing. Check the article to see what happens as the material changes. Hint: it matters!
Tool Crib
You can have the CADCAM Wizards pick tools from a Tool Crib. This is helpful if you want it to stick to the tools you actually have on hand, or if you are using premium tooling and want CADCAM Wizards to capture the manufacturer's specs from that tooling. You just list the cribs you want it to choose from in order. It will use the first tool that works. This allows some interesting possibilities.
For example, you could list a crib corresponding to the machine's toolchanger, followed by what tools you have in inventory, followed by what tools your shop has approved for purchase. That will cause CADCAM Wizards to try to use whats in the toolchanger, followed by whats in inventory, followed by what has been approved for purchase.
Indexable Rough
This is where you specify the available Indexable Roughers you have.
Face Milling
This is where you specify the available Face Mill you have.
Chamfer Tool
This is where you specify your available Chamfer Tool.
Other
At the moment, "Other" controls whether CADCAM Wizards will use your premium coolant options such as through spindle coolant or programmable coolant nozzles.
Lathe Setup Options
Here are the Lathe Setup Options:
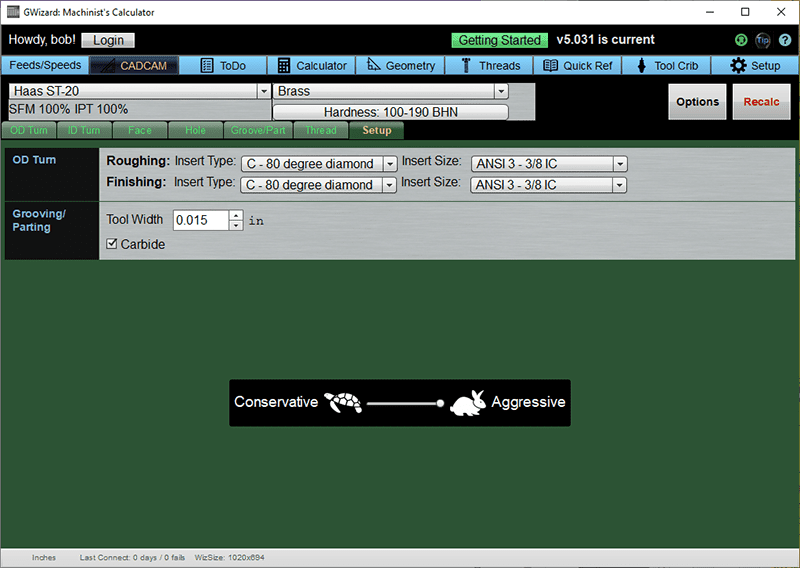
These options basically let you specify the Insert shape and size for the various turning operations.
Individual Wizard Documentation
In this section we'll document what the settings for each individual CADCAM Wizard do. Each Wizard will be shown with all Options enabled. Just click the "Options" button to show all Options if they're aren't showing already.
Milling/Router Wizards
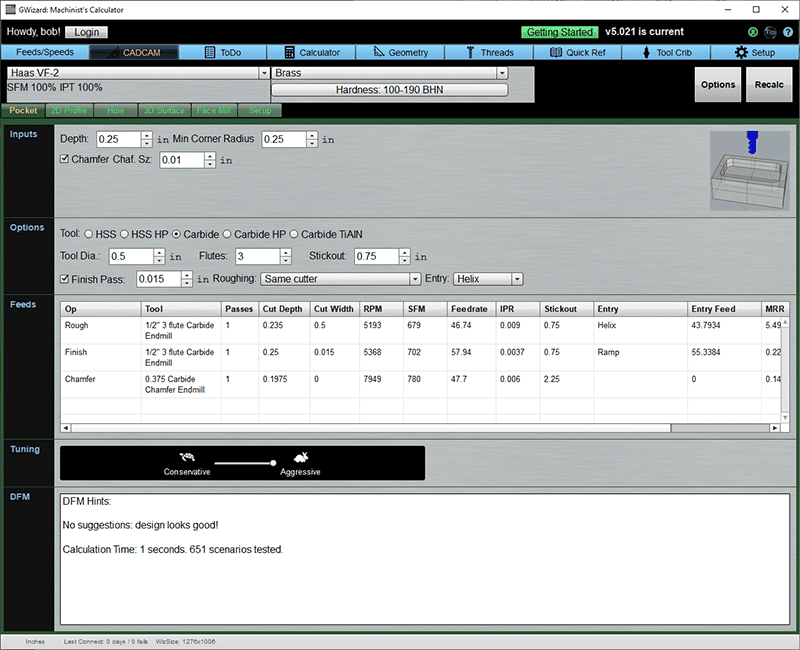
Inputs
Depth: The maximum depth of the pocket.
Min Corner Radius: The smallest inside corner radius of the pocket. This radius limits the maximum size of a finishing tool because it has to fit into that corner radius.
Chamfer: Click to add a chamfer pass.
Chamfer Size: Determines how wide the Chamfer will be.
Options
There are options to override the tool the CADCAM Wizard will select.
Finish pass determines whether there will be a finish pass and how much finish allowance to leave.
Roughing is the roughing strategy. See what those strategies are above.
Entry is the type of entry that will be used. Choices are plunge, helix, and ramp. Helix is the most gentle, followed by ramp, and plunge is least gentle.
2D Profile
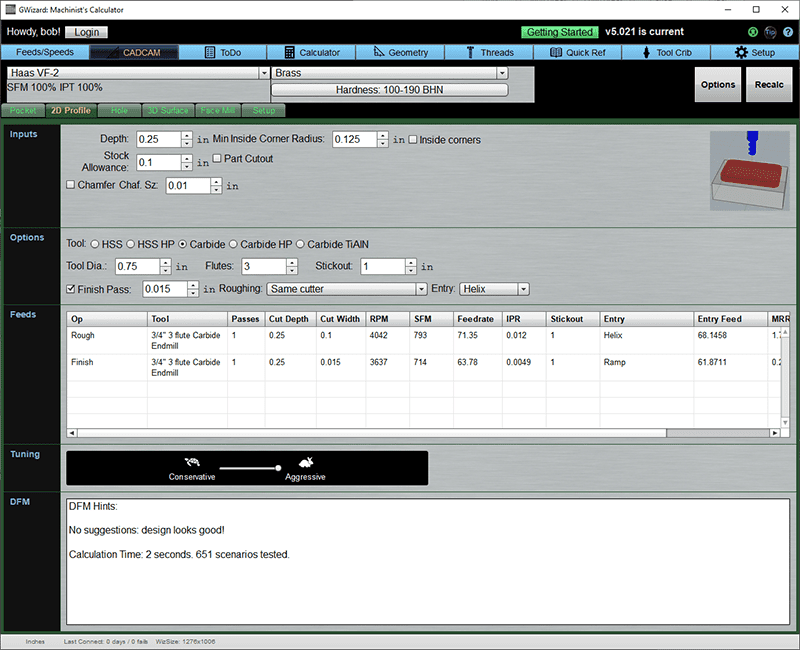
2D Profiles are basically just about cutting the walls. They can also be about cutting out parts from flat sheet, such as on a CNC Router.
Inputs
Depth: The maximum depth to be profiled after all passes. Make it just a little more than what's needed to cut through the material if cutting out parts.
Min Inside Corner Radius: The smallest inside corner radius of the cut. Inside corners are like cul de sacs. If there are no inside corners, don't check the box. This radius limits the maximum size of a finishing tool because it has to fit into that corner radius.
Stock Allowance: If cutting out parts, this is the max distance from edge of workpiece to edge of part.
Chamfer: Click to add a chamfer pass.
Chamfer Size: Determines how wide the Chamfer will be.
Options
There are options to override the tool the CADCAM Wizard will select.
Finish pass determines whether there will be a finish pass and how much finish allowance to leave.
Roughing is the roughing strategy. See what those strategies are above.
Entry is the type of entry that will be used. Choices are plunge, helix, and ramp. Helix is the most gentle, followed by ramp, and plunge is least gentle.
Hole
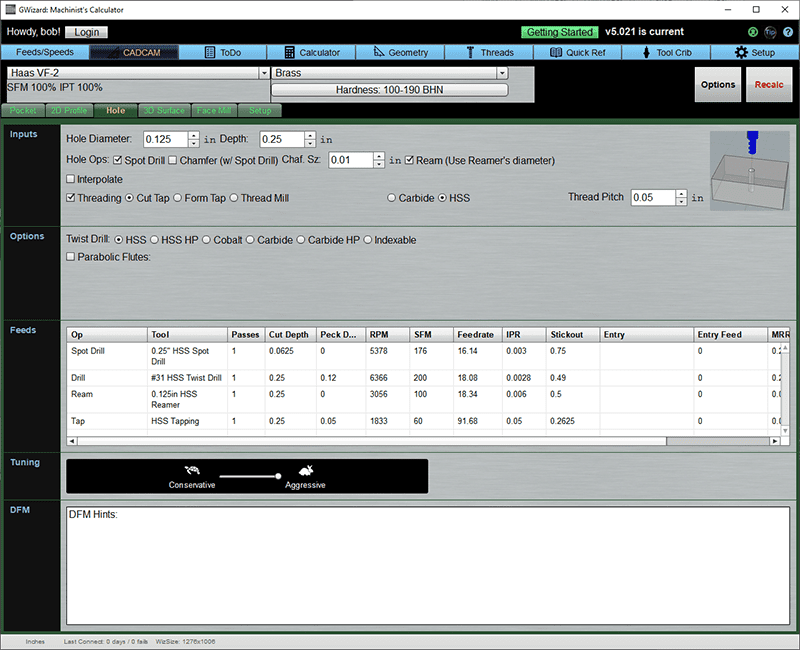
Holes often require multiple operations, so the Hole Wizard is set up to accommodate.
Inputs
Hole Diameter: The diameter of the hole.
Depth: The maximum depth of the hole.
Spot drill: Spotting a hole will ensure the tip of the twist drill doesn't wander. This makes for a more accurate hole location.
Chamfer: Click to add a chamfer pass.
Chamfer Size: Determines how wide the Chamfer will be.
Ream: Reaming the hole will clean up the wall finish and ensure tighter tolerances on the hole diameter. Use the diameter of the reamer (i.e. finished diameter). The CADCAM Wizard will select the appropriate smaller twist drill size for the reamer.
Threading: Many holes need threads. You can cut the threads with a Cut Tap, Form Tap, or Thread Mill. Specificy Carbide or HSS for the tool material. Give the thread pitch as well.
Options
There are options to override the tool the CADCAM Wizard will select.
Select parabolic flutes to force a parabolic flute geometry. Otherwise, G-Wizard will select parabolic flutes if needed.
3D Surface
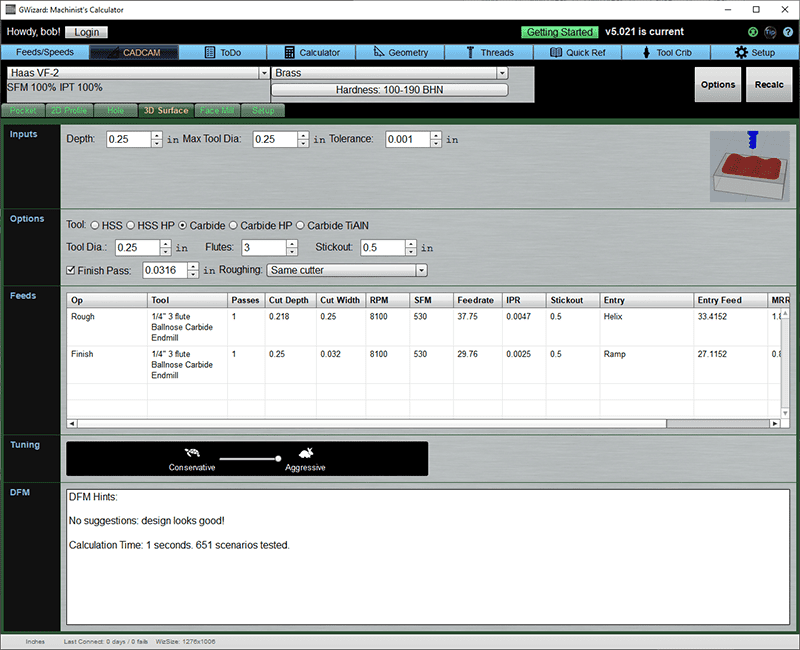
Inputs
Depth: The maximum depth to be profiled after all passes.
Max Tool Dia is the largest tool that will fit into the tightest nooks and crannies of the 3D surface.
Tolerance is the maximum scallop height allowed after machining is complete.
Options
There are options to override the tool the CADCAM Wizard will select.
Finish pass determines whether there will be a finish pass and how much finish allowance to leave.
Roughing is the roughing strategy. See what those strategies are above.
Face Mill
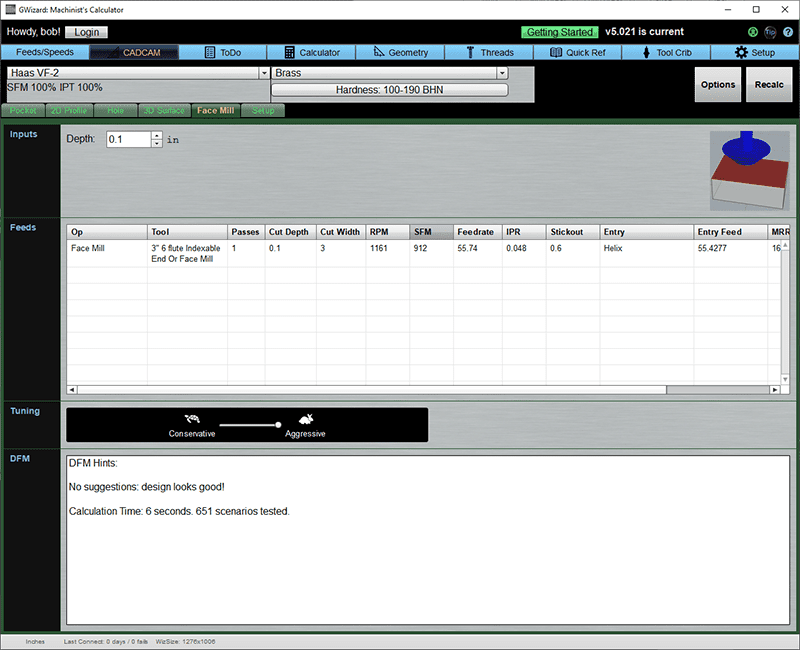
Note that the diameter and flutes of the Face Mill are taken from the Setup parameters.
Inputs
Depth: The maximum depth to be taken off after all passes.
Turning Wizards
OD Turn
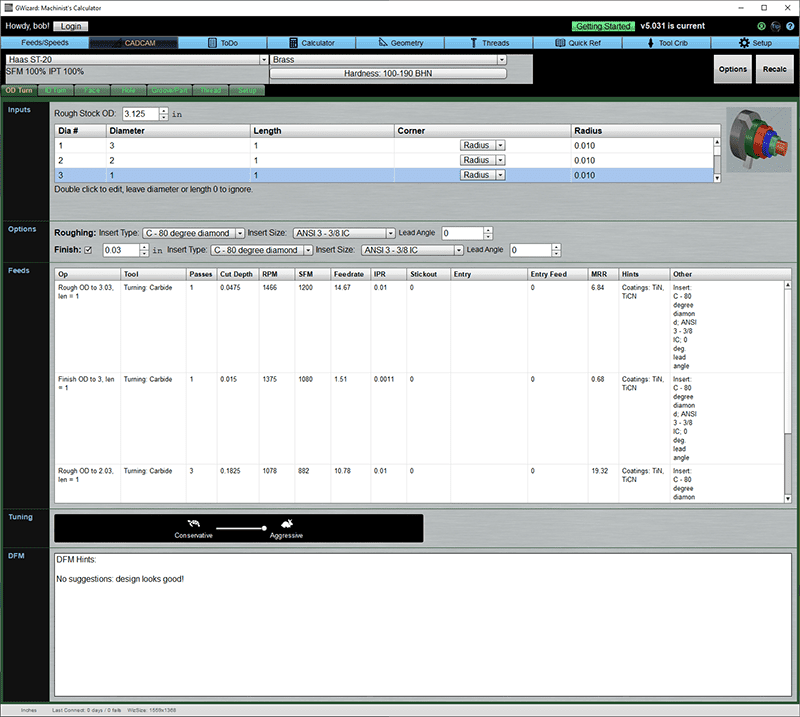
Inputs
Rough Stock OD is the max OD of the rough stock to be turned.
The Input grid lists OD diameters to be turned from left to right. The first entry is the leftmost, in other words. Leaves diameters 0 when you have no more to turn. Diameters must decrease as you go down the list.
You enter the length that each segment of that diameter will be. In addition, you can enter a corner treatment to either radius or chamfer the corner. The Radius column tells the radius of the corner radius or the width of the chamfer.
Options
Options allow you to override the insert type specified in the Turning Options on the Setup tab. They also allow a lead angle, whether or not to have a finish pass, and the insert and lead angle for the finishing tool.
ID Turn
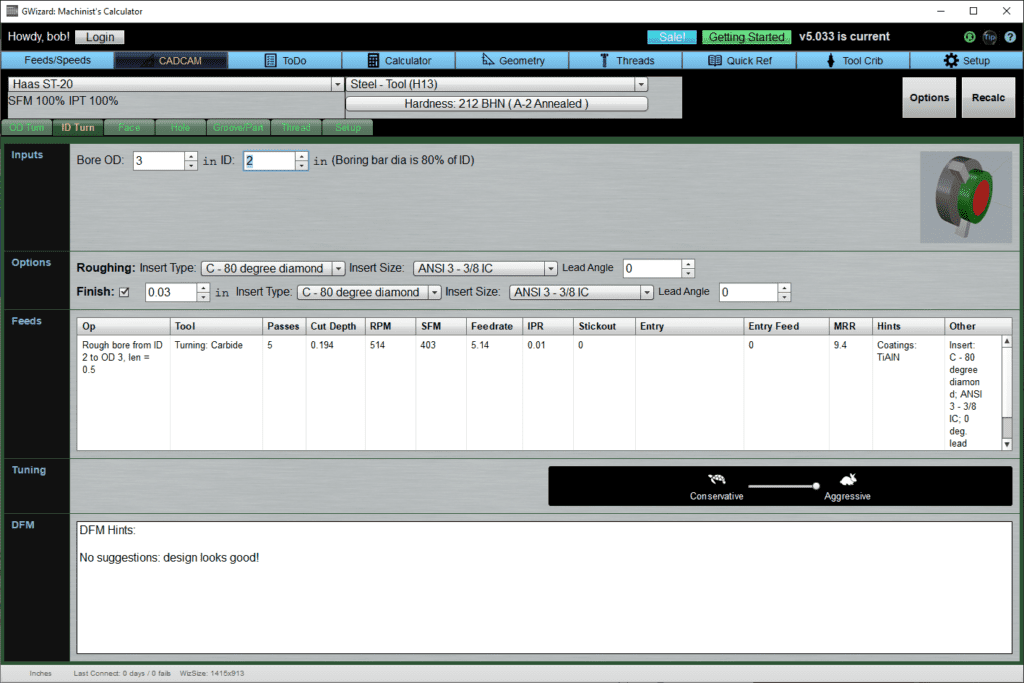
Inputs
Bore ID is the diameter of the initial hole we are starting from. Bore OD is the finished bore diameter.
Options
Options allow you to override the insert type specified in the Turning Options on the Setup tab. They also allow a lead angle, whether or not to have a finish pass, and the insert and lead angle for the finishing tool.
Face

Inputs
Rough Stock OD is the diameter of the rough stock at start of facing op.
ID is how far in to face. Use 0 to face the entire surface.
Z Start is beginning of part, Z End is Z when done facing. Z Start - Z End is how much to remove.
Options
Specify inserts and lead angles for roughing and finishing. Finish pass is optional and can be disabled.
Hole
See the Mill Hole Wizard above as the Turning Hole Wizard is pretty much the same. For single point threading, see the Threading Wizard below.
Groove/Part
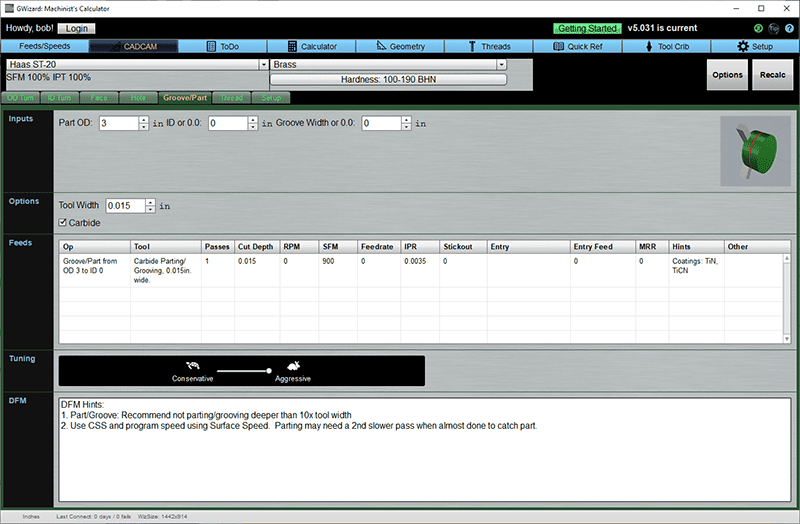
Inputs
OD is the diameter of the stock at start of grooving or parting op.
ID is diameter at end of cut. Use 0 to part off the entire surface. Note, you'll see a hint that suggests you may want to part in 2 passes, with the first pass not cutting all the way and the second running more slowly so the part isn't flung too hard and damaged.
Groove width is the width of the groove. If it is wider than the tool, several passes will be made.
Options
Allows you to change the tool width or specify carbide instead of what's in the Setup Options.
Thread
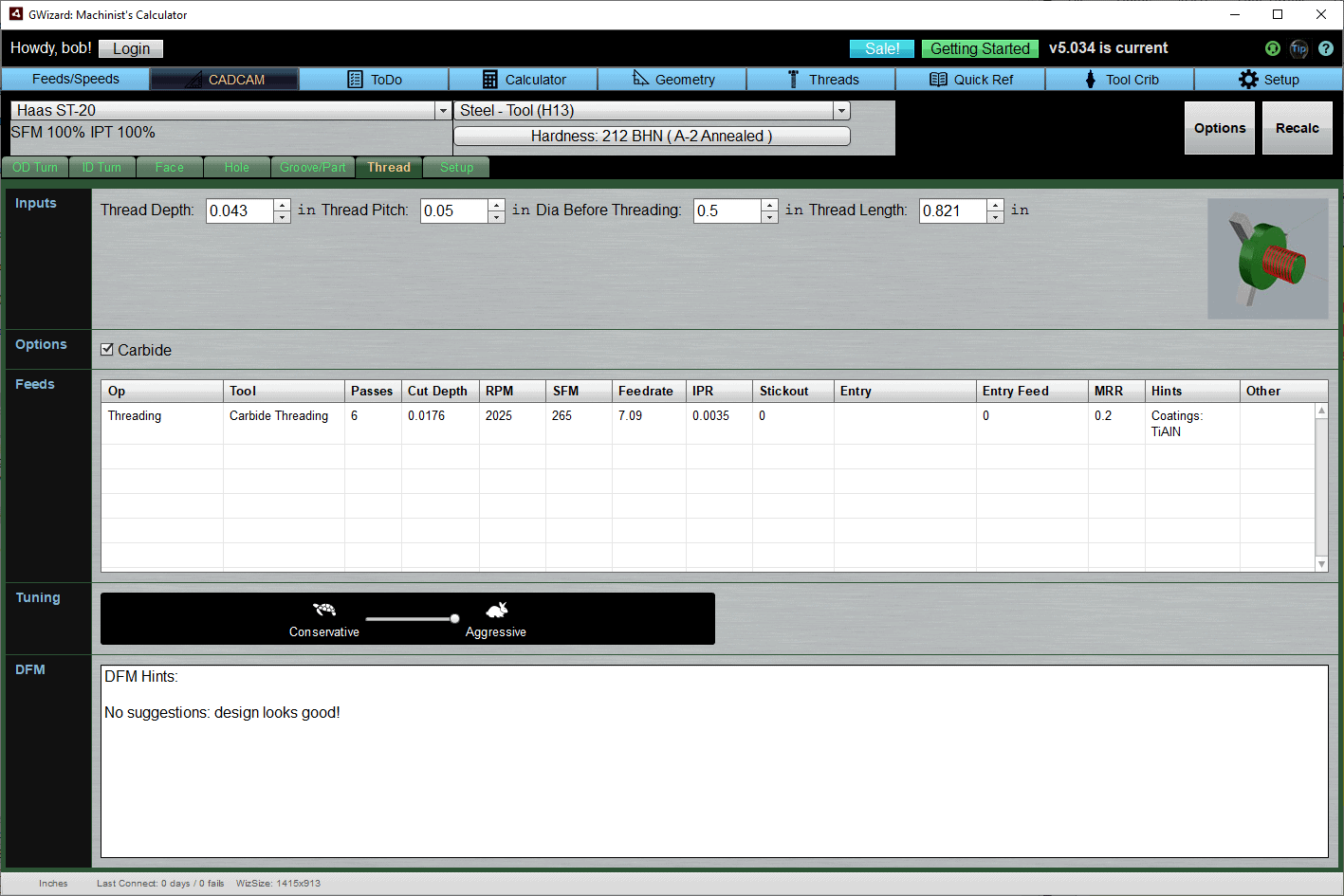
Inputs
Thread Depth is distance from top to deepest part of thread.
Thread Pitch is distance between thread crests.
Dia Before Threading is the workpiece's diameter before threading. Note that it should be the diameter of the flat crest. G-Wizard assumes you will turn to that diameter before threading.
Thread Length is the distance along the axis of the helix to thread.
Note: You can look up most of this information on the Threads tab in G-Wizard
Options
Selecting the Carbide option tells G-Wizard your threading tool is Carbide. Deselecting makes it HSS.
Be the first to know about updates at CNC Cookbook
Join our newsletter to get updates on what's next at CNC Cookbook.