GD&T Tutorial Home GD&T Symbols
Free True Position Calculator [ + Much More ]
Key Takeaways
-
The GD&T Symbol for True Position is a little crosshairs:

GD&T Position Symbol
-
True Position is the total permissible position deviation that a feature can have from its “true” or theoretical position–that is, the total variation from the actual position if there was no error on an ideal part.
-
Here’s the usual True Position Equation for X and Y:
True Position = 2 x SQRT(XVAR^2 + YVAR^2)
-
True Position Explained: Let’s relate that True Position back to convention plus/minus or limit dimensions.
True Position Example: Traditional plus/minus tolerancing must fit inside the yellow square…
-
As the above diagram illustrates, True Position is much more forgiving than traditional plus/minus tolerancing.
-
Rule of thumb: You only have a little more than a third of True Position in each dimension for your plus/minus tolerance. About 35% to be more exact.
-
Using a circular tolerance zone instead of a square one also makes more sense if you think about it. Why are we trying to hit that area? Perhaps because we want a round pin to fit in a round hole. Why then would squares have anything to do with it? GD&T just makes better geometric sense too.
Introduction to GD&T True Position
We'll show you our True Position Calculator in a minute, but first, we want to cover True Position from a learning standpoint.
Here's a quick video description of True Position:
We've picked up a lot of fundamentals in prior chapters. You know how Datums and Feature Control Blocks work, for example. We just finished going over plus/minus tolerancing-the way most drawings that don't use GD&T are toleranced. Now let's put all of that together by taking our first look at the GD&T concepts around tolerancing positions or locations and let's also take a look at the true position formula and using a true position calculator.
GD&T uses a notion called True Position when tolerancing locations. There are two forms of GD&T True Position-one for a feature size under a material condition (Maximum Material Condition or Least Material Condition), and one for True Position Regardless of Feature Size (RFS).
True Positions are relative to Datums, so you will want to spell out which datums in the Feature Control Block are associated with a True Position.
True Position Symbol
The GD&T True Position Symbol is a little crosshairs:

GD&T Position Symbol
Definition of True Position
True Position is the total permissible position deviation that a feature can have from its "true" or theoretical position-that is, the total variation from the actual position if there was no error on an ideal part. Depending on how it is called out, true position can be used in a lot of different ways.
Let's make that simpler with an example. Consider the true position of the center of a hole, a very common application. Let's say the callout gives a true position tolerance of 0.0015". So how far off can the center actually be?
Be careful!
Many who are not familiar with GD&T True Position may jump to the conclusion that they just need to locate within a thou and a half (0.0015") on X and Y and all will be well. But is that really true? To understand the answer, we must understand how to calculate true position:
How to Calculate True Position: True Position Formula
Here's the usual True Position Formula for X and Y:
True Position = 2 x SQRT(XVAR^2 + YVAR^2)
So, we take the difference in X (difference between actual and measured X), square it, add that to the difference in Y squared, take the square root of that sum and multiply by 2.
Let's say we're off by 0.0015 in both X and Y. That gives us the following True Position Calculation Formula:
True Position = 2 x SQRT( 0.0015^2 + 0.0015^2) = 0.004243
We're off from the 0.0015 True Position maximum allowed positional deviation by almost 2x!
Even with half the differences, so X and Y are within 0.00075" of the true center, the True Position still works out to be 0.002121".
True Position can be tougher than it looks on first glance!
Since a picture is worth a thousand words, geometrically, what we've been talking about looks like this:
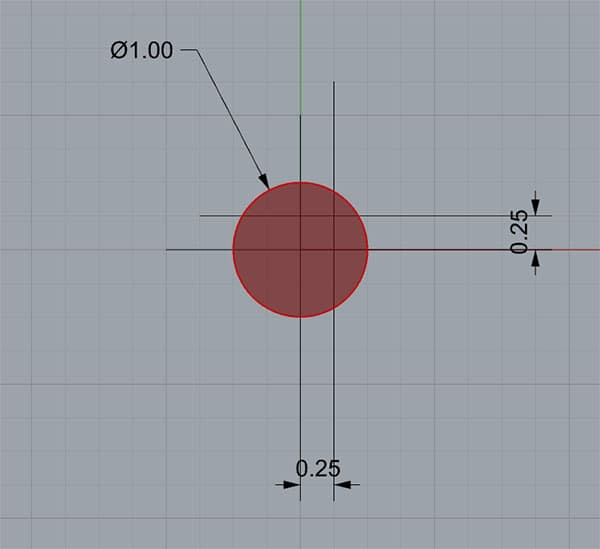
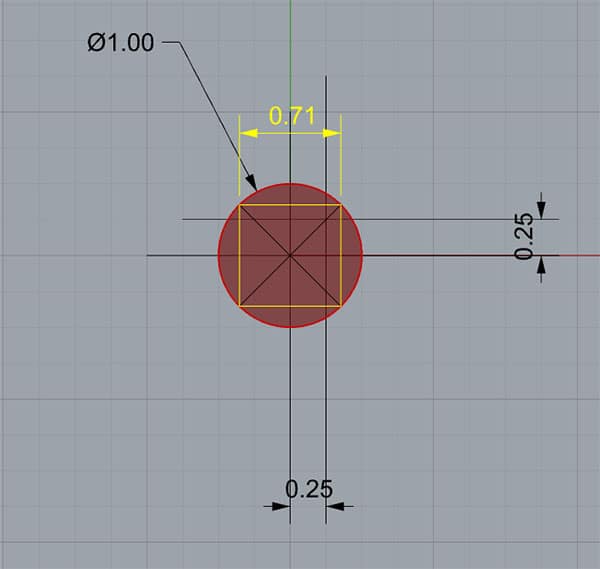
The Red Circle is the tolerance zone for the hole center...
In this example, the Red Circle is the tolerance zone for the hole center. The True Position is 1.00 (keeping it in round numbers to make it easier to scale your real numbers and see what all this means). The actual position of our hole differs from True Position by 0.25 in both X and Y. So the True Position in this example would be 0.7071, which is within the 1.00 position deviation called out for the True Position-we're okay!
Now let's relate that True Position back to convention plus/minus or limit dimensions.

True Position Example: Traditional plus/minus tolerancing must fit inside the yellow square...
If we were using traditional plus/minus tolerancing, we would use something along the lines of the yellow square. It's sides in this case are 0.71" (at this precision, it's actually the square root of 0.5, the circle's radius), so we'd use plus or minus half that to get a position deviation of plus or minus 0.355.
Here's the rule of thumb to memorize:
You only have a little more than a third of True Position in each dimension for your plus/minus tolerance. About 35% to be more exact.
Now you may have heard people say that GD&T actually lets us use looser tolerances so parts are cheaper to make. This diagram makes that clear. If we can only use plus/minus tolerancing, all we can do is use the square, which is forcing us to a smaller area in which our actual hole center must fit: the area of the yellow square is certainly less than the red circle. In fact, it is quite a bit less.
Because we are allowed to hit a larger position deviation with GD&T's True Position concept, it's easier. Look at it this way-the 4 areas of the True Position Tolerance Zone that are outside the plus minus tolerance zone make it clear that there are places where one of the two plus/minus tolerenaces could be broken and the feature would still be within true position tolerance!
Using a circular tolerance zone instead of a square one also makes more sense if you think about it. Why are we trying to hit that area? Perhaps because we want a round pin to fit in a round hole. Why then would squares have anything to do with it? GD&T just makes better geometric sense too.
True Position is More Work to Measure (Unless You Have a CMM or Probe)
But, I hear the wheels turning out there among you, dear readers. You are a little miffed at all the calculating that has to take place using the True Position Formula. You're probably also wondering how long it'll take you to get used to eyeballing numbers like these and having a good feel for what's going on (just remember that 35% figure for comparison!). With the old plus/minus tolerancing, it was easier to measure tolerances and easier to get a gut feel for what was going on.
Well, yes, you are right, but you will get used to it and if you have a probe or CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), they'll do all those pesky True Position Formula calculations for you. In fact, if you even just have G-Wizard, it'll do those pesky calculations too:
G-Wizard True Position Calculator
G-Wizard, our Feeds and Speeds Calculator, is chock full of useful utilities. One of them is a True Position Calculator that will check if you pass the True Position Test:
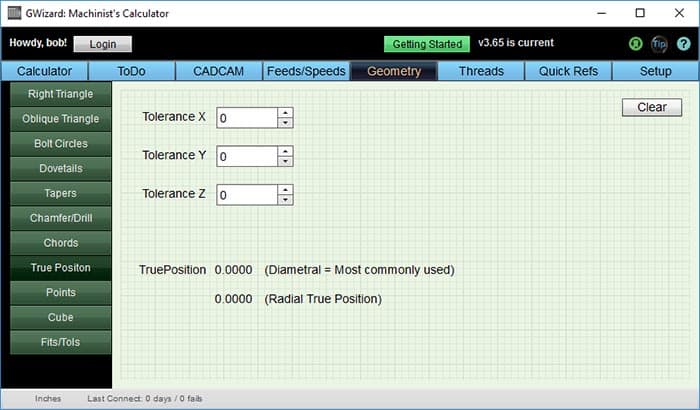
G-Wizard has a handy Position Calculator built right in!
Using the Position Calculator could not be easier. Just enter the difference between actual and ideal position in X, Y, and Z and it'll work through the True Position Formula to tell you True Position. Don't have a Z datum for the True Position? No worries, just leave it 0.
If you're thinking a calculator like G-Wizard might be pretty handy, welcome to the club. There are thousands of CNC'ers who use it every day. But here’s something else–you can get lifetime access to all the reference materials except the Feeds and Speeds Calculator and threads when you buy the 1 year subscription for $79. That’s all it costs to have all the upgrades, customer service, and use of the product for life!
You can see a pretty good collection of the free calculators included such as True Position but also Polar Coordinates Calculator, Triangle Calculators, and much more.
So what’s the catch? Why does anyone ever pay more than $79?
Many hobbyists don’t pay more than $79, BTW. The catch is a spindle power limit. When you buy the 1 year G-Wizard for $79, you get 1 year of unlimited spindle power for Feeds and Speeds. When that expires, you get a spindle power limit of 1 HP. That limit is based on however many years you subscribe for. You can increase it any time you like by renewing the subscription. Or, if you don’t like subscriptions, you can also by the product outright. And we never charge for updates or customer service.
So go ahead, give G-Wizard a free 30 day trial. You’ll be surprised at all the time it saves you on things like True Position, not to mention the other handy reference materials but also the longer tool life, better surface finish, and shorter cycle times you’ll get from better Feeds and Speeds.
Where Can True Position Be Used?
True Position is about tolerancing positions, so it makes sense to use it in terms of an axis, point, or plane. True Position can be 2 or 3 dimensional (and will need an appropriate number of corresponding datums). Usually, you specify the exact point where your position should be and use True Position to tell how far away from that position is acceptible.
Using True Position With Material Conditions (MMC/LMC)
Maximum Material Condition (MMC) is a GD&T symbol that indicates the maximum or minimum allowed tolerance of a feature when it has the maximum amount of material based on volume or size.
- Holes and Bores have MMC = Minimum allowed diameter according to tolerance.
- Shafts and Pins have MMC = Maximum allowed diameter according to tolerance.
When you can combine True Position with Maximum Material Condition (MMC), it allows you to control location, orientation, and size of the feature all at once-GD&T can be very concise! This combination (True Position + Maximum Material Condition) is also helpful for making it easy to create functional gages to inspect the feature on parts.
Combining MMC with True Position means that the maximum allowed position deviation is considered where the features size is at its maximum material condition. As the difference between a feature's measured size and its MMC grows, you can use a bigger tolerance (called a "True Position Bonus Tolerance") on position.
True Position For X or Y (Non-Diameters, No Ø Symbol)
True Position is most commonly used for diameters, for example, to locate the center of a hole. However, when used without the Ø symbol, it just indicates tolerance for an X or Y dimension. In other words, it is the distance from the ideal X or Y.
You don't want to do this very often, particularly if the diameter version could've been used because you're changing those circular tolerance zones into square tolerance zones.
True Position on Drawings: True Position Callout
By now you're grasping the basics of how True Position works. Let's get a good look at how it appears on drawings with an example of a True Position Callout:
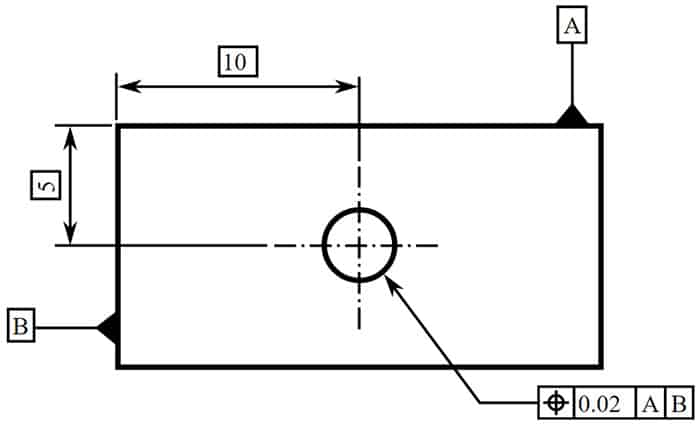
True center position of the hole regardless of feature size...
The drawing above has a hole whose center is at X = 10, Y = 5. The True Position of that center is 0.02. The A and B datums are clearly marked and so things are straightforward.
If we wanted to specify the Maximum Material Condition, that would simply be added to the Feature Control Block. What if we added it hear? Knowing the True Position is at Maximum Material Condition would let us construct a functional pin gage. The diameter of the pin would be the nominal diameter of the hole minus the Maximum Material Condition True Position Tolerance. Likewise, we'd position that pin at X = 10 and Y = 5 since the MMC took care of both size and position for our gage.
Using Maximum Material Condition with True Position can be very handy!
Statistical Process Control for True Position
SPC is a touch beyond the scope of this article, but here's a link to help.
Conclusion
True Position is a pretty nifty alternative to plus/minus tolerances. Not only does it make more geometric sense, it actually allows you to make parts that fit more cheaply because the true position tolerance zone you have to hit (the round circle) is bigger than the typical tolerance zone plus/minus tolerancing allows (the square one). And, with a good Position Calculator, it's easy to get exact values to work from too.
Onward, we've got more GD&T to show you!
GD&T Tutorial Home GD&T Symbols
FAQ
How is true position calculated?
Here's the usual True Position Formula for X and Y:
Ture position = 2 * SQRT(XVAR^2 + YVAR^2)
So we take the difference in X (difference between actual and measured X), square it, and add that to the difference in Y squared. Take the square root of that sum and multiply by 2.
How do you interpret true position?
True position is based on a circular tolerance zone whose center is the theoretical perfect position. If your measurement falls within the circle, then it passes the true position tolerance test.
What is True Position vs Position?
"True Position" refers to the exact position of a feature as defined by basic dimensions. The Position symbol s used to indicate positional tolerance--the allowable amount of variation of that feature from its True Position.
What is the formula for position tolerance?
To calculate position tolerance:
Position tolerance = | Actual Position - True Position |
The result indicates how much the position can deviate from the ideal position while still being accepted.
What is the bonus tolerance for true position?
Bonus tolerance for true position is a GD&T concept that allows you to increase the tolerance zone for a feature based on its actual size. This can help to achieve better functional fit and reduce manufacturing costs.
What is the difference between true position and positional tolerance?
The GD&T "Position Tolerance" is how far your feature's location can vary from its "True Position."
How to calculate the bonus tolerance?
Bonus tolerance equals the difference between the actual feature size and the MMC of the feature.
Be the first to know about updates at CNC Cookbook
Join our newsletter to get updates on what's next at CNC Cookbook.